Many business owners confuse net revenue and profit, assuming that high revenue always equates to success. In reality, understanding the difference between these terms is vital for making sound financial decisions.
Net revenue and profit are distinct metrics, and both play crucial roles in forecasting, strategic planning, and assessing a business’s sustainability. This guide provides a comprehensive look at these concepts, their differences, and how business owners can use them to improve their financial performance.
What Is Revenue?
Revenue is the total income a business earns from its sales of goods or services. It appears at the top of the company’s income statement, which is why it is often referred to as the top line. Revenue measures the total amount of money coming into the business before expenses are deducted.
Types of Revenue
Gross revenue. The total income from all sales of goods and services without accounting for refunds, discounts, or allowances. For example, if a company sells 200 items at $50 each, its gross revenue is $10,000.
Net revenue. Gross revenue minus refunds, discounts, and allowances. If $1,000 in discounts apply to the example above, the net revenue is $9,000.
Why Revenue Is a Top-Line Metric
Revenue shows how much money your business generates through its operations. It helps track growth and indicates the scale of your business activities, making it a key metric for forecasting. However, revenue doesn’t reveal whether the business is profitable. To assess financial sustainability, you need to look at profit.
What Is Profit?
Profit is what remains after all costs and expenses have been subtracted from revenue. Profit is also known as the bottom line and reflects the business’s ability to sustain operations, cover costs, and generate value for owners and investors.
Types of Profit
Gross profit. Net revenue minus cost of goods sold (COGS). Gross profit measures the efficiency of production or service delivery by subtracting direct costs like raw materials and labor from revenue.
Operating profit. Gross profit minus operating expenses. This type of profit includes costs like rent, utilities, and salaries, reflecting the income from regular business operations before taxes and interest.
Net profit (or net income). The total income remaining after deducting all expenses, taxes, and non-operating revenue. This bottom line figure is the clearest indicator of a company’s profitability.
Why Profit Matters
Profit determines whether your business is financially sustainable. Even with high revenue, poor cost management can result in net loss. Profit is also critical for cash flow, funding growth initiatives, and making strategic decisions about the future.
Revenue vs Profit: Key Differences
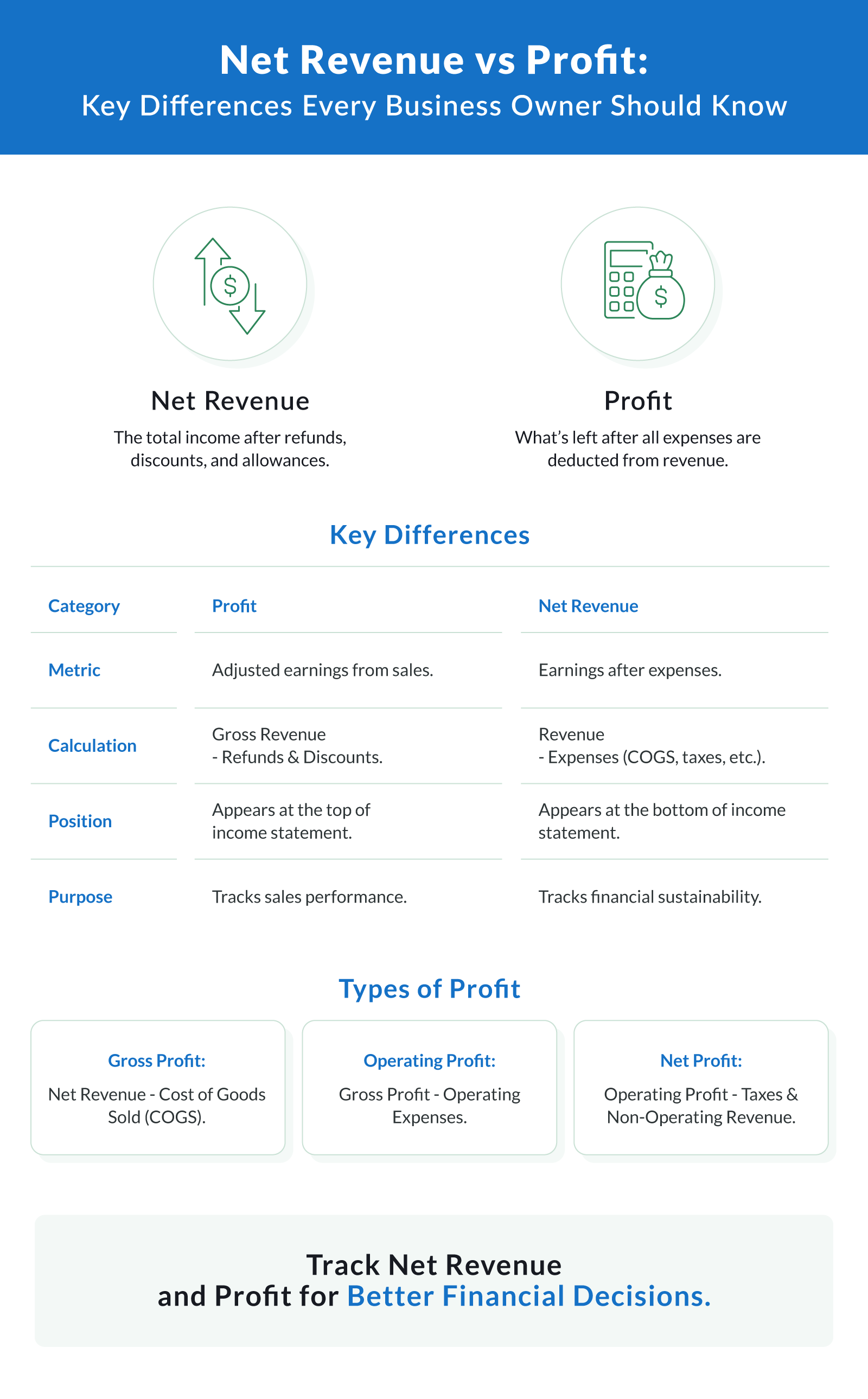
Understanding the distinction between revenue and profit is essential for small business owners and startups. While both are important, they serve different purposes in evaluating financial performance.
Revenue measures total income, and profit measures what's left. Revenue represents the total sales of goods or services, while profit shows how much of that income remains after expenses.
Revenue is about growth, and profit is about sustainability. Revenue growth indicates increasing sales, but without proper cost control, it won’t lead to long-term financial health.
Revenue supports operations, and profit fuels decisions. Revenue drives day-to-day business activities, while profit informs strategic decisions like investments and expansion.
Where Revenue and Profit Appear on Financial Statements
Revenue and profit are both tracked on the income statement, a key document in financial reporting.
Revenue. Appears at the top as gross or net revenue. It is the starting point for calculating other metrics like gross profit margin.
Profit. Appears at the bottom, broken into gross profit, operating profit, and net profit. These figures provide insights into different aspects of the company’s profitability.
Analyzing these numbers helps business owners make informed decisions and identify areas for improvement.
Common Challenges Business Owners Face
Many business owners and startups make mistakes when managing revenue and profit. Here are some common challenges:
Focusing only on revenue. High revenue doesn’t guarantee profitability. Without tracking costs, a business can have high revenue but still experience a net loss.
Overlooking cost of goods sold (COGS). Direct costs like raw materials and labor directly impact gross profit. Ignoring these expenses can skew financial planning.
Failing to control operating expenses. High overhead costs, such as rent and payroll, can erode operating profit, even if gross profit is strong.
Misinterpreting financial metrics. Revenue alone doesn’t provide a full picture of the company’s financial health. Monitoring profit margins and other metrics is essential.
Tips for Business Owners
Improving your business’s profitability and financial health requires focusing on both revenue and profit. Consider these strategies:
Track both revenue and profit. Use tools to monitor financial metrics like gross profit margin and net profit margin.
Control costs. Regularly review COGS and operating costs to identify opportunities for savings.
Focus on sustainable growth. Balance revenue growth with efforts to maintain healthy profit margins.
Analyze financial statements. Review your income statement to evaluate financial performance and identify trends.
Refine pricing strategies. Ensure your pricing reflects both market conditions and the costs of producing your goods or services.
Leverage automation. Automate bookkeeping and financial reporting to streamline operations and improve accuracy.
Why This Matters for Startups and Small Businesses
For startups and small businesses, understanding the difference between revenue and profit is critical. Many startups focus heavily on revenue growth to attract investors but fail to achieve sustainable profitability. Balancing growth with cost control ensures long-term success.
Accurate financial reporting and automation can make it easier to track revenue and profit, allowing you to focus on strategic decisions.

Final Thoughts
Revenue and profit are essential for understanding your business’s financial performance. While revenue shows the total amount of money your business generates, profit reveals whether your business is truly sustainable. By tracking these metrics, managing costs, and analyzing financial statements, small business owners can make better decisions and build stronger businesses.
Ready to Improve Your Financial Health?
If your business needs funding to grow and improve profitability, we’re here to help. Apply for funding today at Clarify Capital and take the next step toward success!

Bryan Gerson
Co-founder, Clarify
Bryan has personally arranged over $900 million in funding for businesses across trucking, restaurants, retail, construction, and healthcare. Since graduating from the University of Arizona in 2011, Bryan has spent his entire career in alternative finance, helping business owners secure capital when traditional banks turn them away. He specializes in bad credit funding, no doc lending, invoice factoring, and working capital solutions. More about the Clarify team →
Related Posts





