Price elasticity of demand (PED) measures how a change in price affects the quantity of a product consumers are willing to buy. It's one of the most important concepts in microeconomics, helping businesses and economists predict how pricing changes will impact demand, total revenue, and profitability.
This guide includes a simple price elasticity of demand calculator and a quick breakdown of PED types, formulas, and real-world examples. You'll learn how to use the midpoint method to calculate elasticity, interpret whether demand is elastic, inelastic, or unitary, and apply these insights to build stronger pricing strategies.
Whether you're adjusting prices, forecasting demand, or learning the basics of the demand curve, this tool can help you make data-backed decisions.
Price Elasticity of Demand Calculator
This easy-to-use tool calculates price elasticity of demand. Just enter your initial and new prices and quantities, and the calculator will instantly show your PED, along with whether demand is elastic, inelastic, or unitary. This can help you understand how sensitive your customers are to price changes so you can make smarter pricing decisions.
The PED calculator is useful for:
Business owners reviewing pricing strategies
Students studying microeconomics
Pricing analysts modeling revenue impact
What Is Price Elasticity of Demand?

Price elasticity of demand measures how much the quantity demanded of a product changes in response to a change in its price. It helps explain consumer behavior: When prices go up or down, how likely are customers to adjust how much they buy?
Economists and business owners use PED to forecast revenue, optimize pricing, and understand shifts in the demand curve. In microeconomics, it's a foundational concept for analyzing how pricing decisions impact total revenue.
The basic idea is simple: If a small price change leads to a big change in quantity demanded, the product is elastic. If quantity barely changes, the product is inelastic.
The following formula is used to calculate PED:
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED) = (% Change in Quantity Demanded) / (% Change in Price)
Types of Elasticity: What the Results Mean
Once you calculate the price elasticity of demand (PED), it's time to interpret the result. The number tells you how sensitive customers are to price changes, and what effect those changes have on total revenue.
Here's what each type of elasticity means in practice:
Elastic demand (PED > 1). Consumers respond strongly to price changes. A small price increase can cause a large drop in quantity demanded, potentially decreasing total revenue. Example: Luxury items, non-essential electronics, or trendy fashion products.
Inelastic demand (PED < 1). Consumers are less sensitive to price changes. Quantity demanded changes only slightly, so raising prices may increase total revenue. Example: Gasoline, prescription drugs, and basic food staples — classic inelastic goods.
Unitary elastic (PED = 1). Price and quantity move in exact proportion, so total revenue stays the same regardless of a price change. Example: Products near a balanced demand curve, like certain mid-range household items.
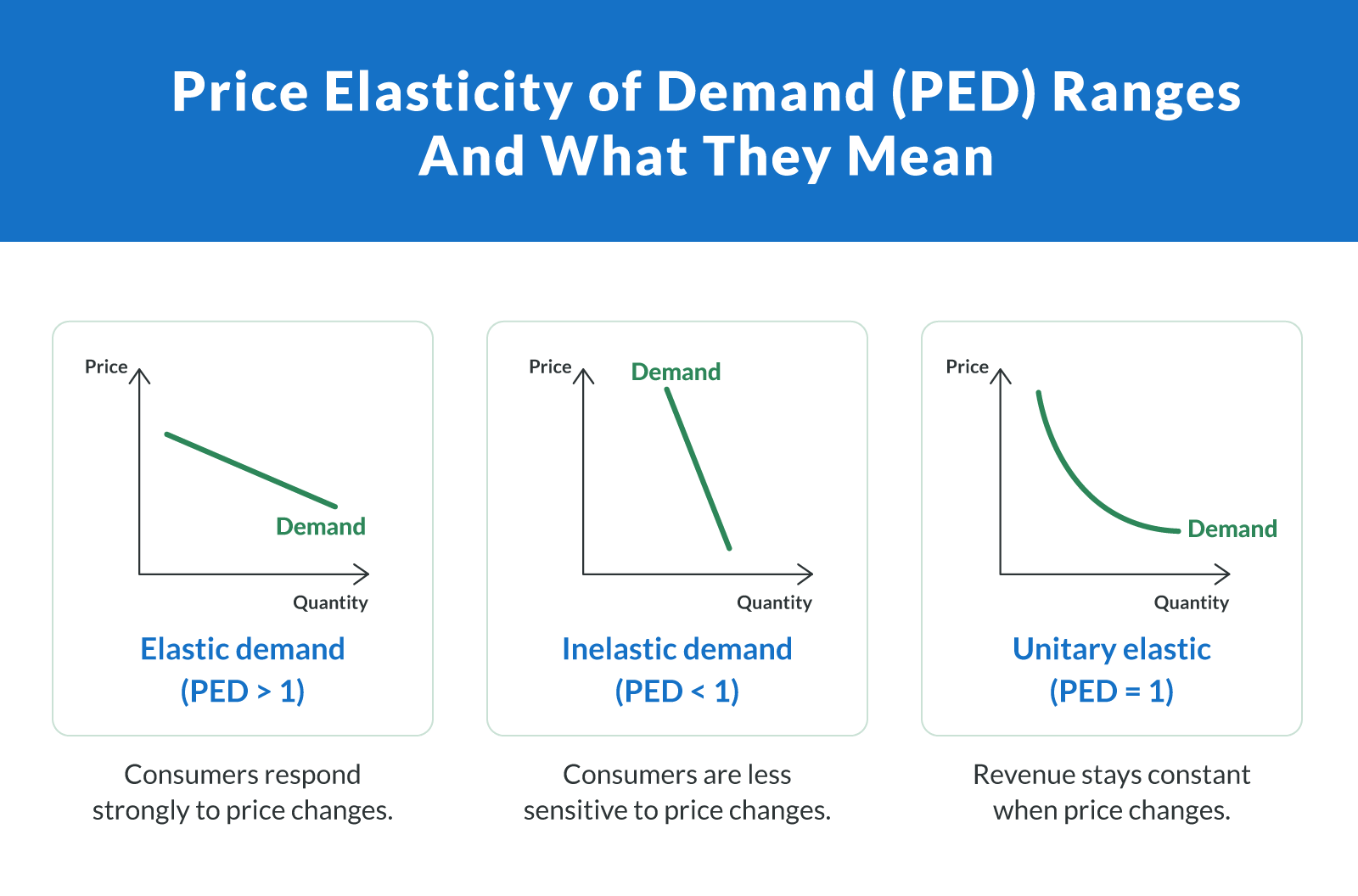
Knowing where your product falls on the elasticity scale helps you decide whether a price increase or decrease is likely to grow or shrink revenue.
Ready to invest in new equipment to meet growing demand?
Clarify Capital provides affordable equipment financing options that help business owners expand without draining their working capital.
What Affects Price Elasticity?
Several things influence how elastic or inelastic a product's demand will be. Understanding them can help you anticipate customer behavior when making pricing decisions:
Availability of substitutes. The more alternatives available, the more elastic the demand. Customers will switch if your price goes up.
Necessity vs. luxury. Essential items (like medication or utilities) are generally inelastic. Luxury goods tend to be more elastic.
Time period. Demand often becomes more elastic over time as customers adjust or find alternatives.
Price point. Items with higher prices usually face more elastic demand since price changes have a bigger absolute impact.
Product category. Some categories consistently show stable demand regardless of price shifts, especially when products are unique or habit-forming.
These insights are key for economists, marketers, and business owners shaping demand curve models and pricing strategies.
Using PED To Improve Pricing Strategy

Understanding price elasticity of demand can help business owners make smarter pricing decisions, boost total revenue, and respond quickly to shifts in customer behavior. Whether you're weighing price increases or price decreases, elasticity insights give you a roadmap for protecting your margins and growing your business.
Here are a few practical ways to apply PED to real-world pricing strategies:
Raise prices carefully on inelastic products to maximize revenue. When demand changes very little after a price increase, you can grow total revenue without losing many sales. Look at the initial quantity sold, forecast the final quantity after the change, and estimate the percentage change to guide your decision.
Lower prices on elastic products to drive higher sales volume. When customers respond strongly to lower prices, a small price decrease can lead to a large increase in the quantity sold, helping you achieve a revenue increase overall.
Protect revenue on unitary elastic products by maintaining stable pricing. If the percentage change in quantity matches the percentage change in price, total revenue stays about the same. In these cases, focusing on operational improvements may have a bigger impact than adjusting prices.
Use elasticity to model different pricing scenarios. By comparing your initial price, final price, initial quantity, and expected final quantity, you can better predict how different price points will impact demand changes and total revenue.
Test and adjust pricing based on actual results. PED gives you a strong starting point, but real-world data matters. Watch how customers respond after a price adjustment and refine your strategy accordingly.
Building pricing strategies with elasticity in mind helps you move from guesswork to data-driven decisions and positions your business for smarter, more sustainable growth.
Thinking about adjusting your prices to boost revenue?
Clarify Capital offers fast working capital loans and flexible lines of credit to help small businesses manage cash flow while testing new pricing strategies.
Understanding Elasticity for Smarter Pricing Decisions
Price elasticity of demand is a tool for small businesses looking to make confident, informed pricing moves. Whether you're launching a new product, responding to competitors, or planning a price adjustment, elasticity insights help you predict customer behavior and protect total revenue.
Bookmark this quick guide and the elasticity calculator for future use. Having a fast way to estimate demand curve reactions will help you make better pricing decisions and stay ahead of changes in the market. Economists, pricing teams, and business owners alike rely on PED models to turn small changes into major advantages.
Ready to put your insights into action and fund your next business move? Apply with Clarify Capital and get matched with fast, flexible financing options built for small businesses.

Michael Baynes
Co-founder, Clarify
Michael has over 15 years of experience in the business finance industry working directly with entrepreneurs. He co-founded Clarify Capital with the mission to cut through the noise in the finance industry by providing fast funding and clear answers. He holds dual degrees in Accounting and Finance from the Kelley School of Business at Indiana University. More about the Clarify team →
Related Posts





