Is tracking total sales enough to know how well your business is performing? Not quite. While many business owners focus on total revenue, understanding the difference between revenue and net sales can give you a much clearer picture of financial health.
Net sales provide a more accurate look at actual earnings after accounting for things like sales returns and discounts. Knowing how both metrics work — and where they show up on your financial statements — is essential for proper financial reporting and long-term planning.
In this article, we'll explain what net sales and revenue mean, how they connect to key financial metrics, and why both numbers matter when evaluating your company's profitability. You'll also learn how to calculate net sales and spot common differences between these two important figures. To wrap up, there's a quick comparison table to help you easily tell them apart.
Let's break down the basics so you can track your sales performance more effectively.
What Are Net Sales?

Net sales are a company's total revenue, excluding sales returns, allowances, and discounts. This figure represents a business's actual income earned from sales transactions after factoring in any reductions. By removing these deductions, the net sales figure more accurately reflects true earnings from goods or services sold.
Net sales appear on a company's income statement, typically listed just below gross sales. They are a critical number for business owners to watch because they show the real strength of your sales efforts without the distortions caused by refunds or discounts.
Tracking net sales can help you:
Better understand your financial health
Improve forecasting
Identify areas where sales performance could be slipping
It also ties into other, broader financial statements, making it easier to assess the overall success of your business operations. Without a clear net sales figure, financial reporting can lead to poor strategic decisions and oversights.
Why Net Sales Matter for Your Business
Net sales connect directly to key performance metrics that measure your business's financial health. Tracking net sales consistently can drive better decision-making and stronger profitability.
Here's why it matters:
Helps calculate gross profit. Net sales are used to determine gross profit, a critical measure of how efficiently your business produces and sells products.
Connects to net income. Since net sales directly influence net income, monitoring this figure helps you evaluate the company's profitability.
Improves cash flow management. A clear view of actual sales performance helps you predict and control cash flow more effectively.
Strengthens financial metrics. Key financial metrics become more accurate and actionable when based on real sales performance rather than inflated figures.
Supports better decision-making. Accurate net sales data informs marketing, product development, and operational improvements.
Provides a true view of the bottom line. Understanding net sales helps you see your real earnings potential and overall financial health.
How To Calculate Net Sales

Wondering how to calculate net sales? It's simpler than it sounds, but extremely important for accurate financial reporting. Net sales give you a true view of the revenue you've earned from the sales of goods after adjusting for any sales returns, allowances, and sales discounts.
Here's the basic sales formula you'll need to calculate it:
Net Sales = Gross Sales − Sales Returns − Allowances − Discounts
To see how this works, let's look at a small business example:
Suppose a business has $100,000 in gross sales during a given period. Over that same period, they experience $5,000 in sales returns and grant $3,000 in sales discounts. Using the formula:
$100,000 − $5,000 − $3,000 = $92,000 Net Sales
This $92,000 net sales figure represents the actual earnings from customer transactions once all reductions are accounted for.
Calculating net sales accurately ensures your financial statements reflect the real performance of your sales activity, making it easier to assess financial health and profitability. For small business owners, monitoring net sales regularly helps with tracking trends over any given period and making smarter business decisions based on financial data.
What Is Revenue?
Revenue, often referred to as total revenue, is the total amount of money a company earns from its primary business activities before any deductions like returns, allowances, or discounts. It's a broad measure that includes all income sources from selling products, providing services, or earning royalties and investment income.
Revenue is frequently called the top line because it appears at the very top of a company's income statement, and it's the starting point for analyzing profitability.
There are several types of revenue you should understand:
Gross revenue. This is the total income from all sources before accounting for any expenses or reductions.
Operating revenue. This income is generated through a company's core business operations, such as product sales or service fees.
Sales revenue. This is the total revenue earned specifically from the direct sale of goods or services to customers.
Other income sources. This may include investment returns, rental income, or one-time sales, depending on the nature of the business.
Revenue shows a business's full earning power across all income sources. Whether you're tracking product sales or service contracts, regularly monitoring total revenue gives you a clear view of your company's long-term financial strength.
A solid understanding of total revenue makes it easy for business owners to set accurate budgets, create forecasts, or make informed investment decisions.
Why Revenue Matters for Your Business
Every business owner who wants to grow their company and maintain strong financial health should track their revenue, since revenue guides budgeting, investment, and operational strategies.
Here's what it helps you do:
Drive business planning. Knowing your total revenue can help you plan future investments, manage operations, and allocate resources wisely.
Measure market strength. Consistent revenue growth often indicates that your products or services are in high demand and your market position is improving.
Improve financial reporting. Accurate revenue figures are critical when preparing financial statements and tax documents for regulatory compliance.
Influence investor decisions. Lenders and investors often use revenue data to assess a company's financial health and profitability potential.
Support profitability analysis. Total revenue sets the baseline for calculating important profitability metrics like gross profit, operating income, and net income.
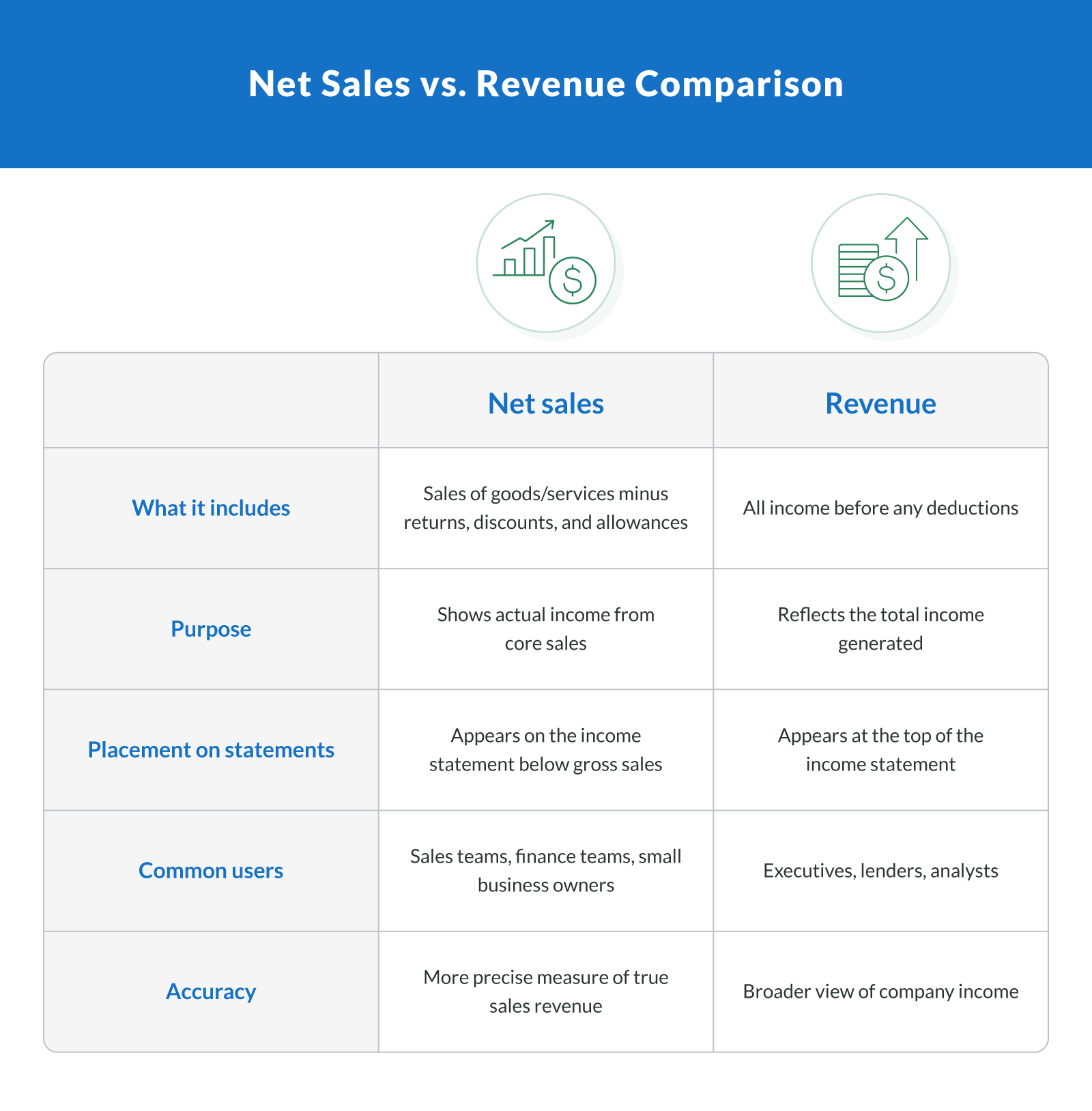
Net Sales vs. Revenue: What's the Difference?
While net sales and revenue are closely related, understanding the key differences is important for accurate financial reporting. Although people sometimes use the terms interchangeably, they are not exactly the same — they are related but distinct concepts.
Here's a quick breakdown of the differences:
Revenue represents the total income earned by a business before subtracting any sales returns, allowances, or discounts.
Net sales are a portion of revenue — specifically the total sales of goods or services after accounting for reductions like returns and discounts.
Revenue includes multiple income sources, such as product sales, service fees, and investment income.
Net sales focus solely on core product or service sales and give a cleaner view of actual earned income.
Revenue appears at the top of the income statement, while net sales show up after gross sales, adjusted for reductions.
In short, net sales are a subset of total revenue. While gross sales reflect the company's total sales without any deductions, the net sales figure subtracts out sales returns, allowances, and discounts to show the real income from sales transactions. This distinction is important when analyzing cost of goods sold (COGS), gross profit margin, and preparing reliable financial statements.
Here's a quick visual to show the comparison:
Mastering Sales Metrics for Smarter Business Growth
Accurately tracking both net sales and revenue helps you maintain your company's financial health. These metrics play a major role in financial reporting, helping business owners make smarter decisions about budgeting, forecasting, and long-term planning. Without a clear view of sales performance, it's easy to miss signs of trouble or overlook opportunities for growth.
To track the right sales metrics, business owners should:
Use CRM tools to organize customer and sales data, making it easier to monitor performance over time.
Integrate accounting software to automatically track gross sales, net sales, and revenue across any given period.
Regularly review financial reporting to compare trends, spot discrepancies, and ensure your financial statements reflect real-world operations.
Pay close attention to net sales, revenue, and related metrics, business owners to improve cash flow management, boost profitability, and strengthen your company's financial health for the long haul.
Ready to strengthen your business finances and fuel future growth? Apply for funding with Clarify Capital today.

Michael Baynes
Co-founder, Clarify
Michael has over 15 years of experience in the business finance industry working directly with entrepreneurs. He co-founded Clarify Capital with the mission to cut through the noise in the finance industry by providing fast funding and clear answers. He holds dual degrees in Accounting and Finance from the Kelley School of Business at Indiana University. More about the Clarify team →
Related Posts





